- #1
Scoop6
- 4
- 0
I need some help with light rays. I've been sick and missed the last few days so I need a little help. I have some questions that I have to submit online by tomorrow. I was wondering if someone could help.
1)
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at a 45° angle of incidence. The mirror is then rotated by = 10° into the position shown in red in the drawing, while the incident ray is kept fixed.
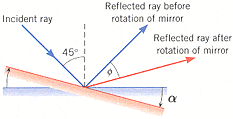
(a) Through what angle does the reflected ray rotate?
(b) What is the answer to part (a) if the angle of incidence is 60° instead of 45°?
Is there some equation for this one? I wasnt sure if you just add 10°. I don't think that's it. I don't have my physics book either so I can't really read through what we have been doing.
-------------
2)
A candle is placed 15.0 cm in front of a convex mirror. When the convex mirror is replaced with a plane mirror, the image moves 8.0 cm farther away from the mirror. Find the focal length of the convex mirror.
on this one i was trying this with the 1/Do + 1/Di = 1/f but wasnt getting anything out of it.
I really need an answer tonight. I appreciate any help. Thanks.
1)
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at a 45° angle of incidence. The mirror is then rotated by = 10° into the position shown in red in the drawing, while the incident ray is kept fixed.
(a) Through what angle does the reflected ray rotate?
(b) What is the answer to part (a) if the angle of incidence is 60° instead of 45°?
Is there some equation for this one? I wasnt sure if you just add 10°. I don't think that's it. I don't have my physics book either so I can't really read through what we have been doing.
-------------
2)
A candle is placed 15.0 cm in front of a convex mirror. When the convex mirror is replaced with a plane mirror, the image moves 8.0 cm farther away from the mirror. Find the focal length of the convex mirror.
on this one i was trying this with the 1/Do + 1/Di = 1/f but wasnt getting anything out of it.
I really need an answer tonight. I appreciate any help. Thanks.
Last edited: