- #1
Buddha
- 4
- 0
Hey guys, I was assigned a bunch of questions by my teacher and I'm having trouble with these two:
A person is sitting with one leg outstretched, so that it makes an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal, as the drawing indicates. The weight of the leg below the knee is 44.5 N with the center of gravity located below the knee joint. The leg is being held in this position because of force M applied by the quadriceps muscle, which is attached 0.100 m below the knee joint. Obtain the magnitude of M.
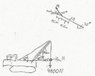
A wrecking ball (weight=4800N) is supported by a boom, which may be assumed to be uniform and has a weight of 3600N. As the drawing shows, a support cable runs from the top of the boom to the tractor. The angle between the support cable and the horizontal is 32 degrees, and the angle between the boom and the horizontal is 48 degrees. Find the tension in the support cable and the magnitude of the force exerted on the lower end of the boom by the hinge.
Hopefully the pictures show up...
A person is sitting with one leg outstretched, so that it makes an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal, as the drawing indicates. The weight of the leg below the knee is 44.5 N with the center of gravity located below the knee joint. The leg is being held in this position because of force M applied by the quadriceps muscle, which is attached 0.100 m below the knee joint. Obtain the magnitude of M.
A wrecking ball (weight=4800N) is supported by a boom, which may be assumed to be uniform and has a weight of 3600N. As the drawing shows, a support cable runs from the top of the boom to the tractor. The angle between the support cable and the horizontal is 32 degrees, and the angle between the boom and the horizontal is 48 degrees. Find the tension in the support cable and the magnitude of the force exerted on the lower end of the boom by the hinge.
Hopefully the pictures show up...