- #1
mathewings
- 8
- 0
Below is the first in a series of questions that build on one another; however I cannot solve this initial one. Any help is appreciated.
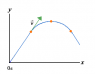
A physics student on Planet Exidor throws a ball, and it follows the parabolic trajectory shown. The ball's position is shown at 1.00 s intervals until t=3.00 s. At t=1.00 s, the ball's velocity is v=(1.95i+2.32j) m/s. Determine the ball's velocity at t=0.00 s. (Enter your answer in component form. Input the x-component first, followed by the y-component.)
A physics student on Planet Exidor throws a ball, and it follows the parabolic trajectory shown. The ball's position is shown at 1.00 s intervals until t=3.00 s. At t=1.00 s, the ball's velocity is v=(1.95i+2.32j) m/s. Determine the ball's velocity at t=0.00 s. (Enter your answer in component form. Input the x-component first, followed by the y-component.)