- #1
nylonman
- 11
- 0
Confusion with 2D DFT
Hello everyone,
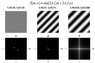
I'm trying to figure out why the third transform in the picture I attach here is different to the other ones, why it's 'distorted'. I know that it's related with the fact that if you copy the image in a grid the resulting image has discontinuous lines, unlike the other two transforms where the resulting lines are continuous, but I can't see the relation with the distortion.
Thank you for any help!
Hello everyone,
I'm trying to figure out why the third transform in the picture I attach here is different to the other ones, why it's 'distorted'. I know that it's related with the fact that if you copy the image in a grid the resulting image has discontinuous lines, unlike the other two transforms where the resulting lines are continuous, but I can't see the relation with the distortion.
Thank you for any help!
Attachments
Last edited: