- #1
bhenchodd
- 4
- 0
Hi fellow members, I would appreciate if you could help with the following problem, it has had me stumped!
Prove the statistical distance between random variables X & Y
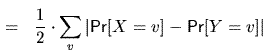
Thank You, and have a great day!
Prove the statistical distance between random variables X & Y
Thank You, and have a great day!