- #1
samieee
- 67
- 0
For a no load ideal transformer
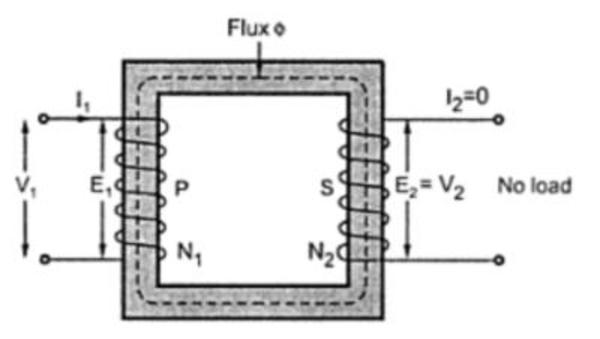
V1 is anti phase with E1?

or
in phase like this?
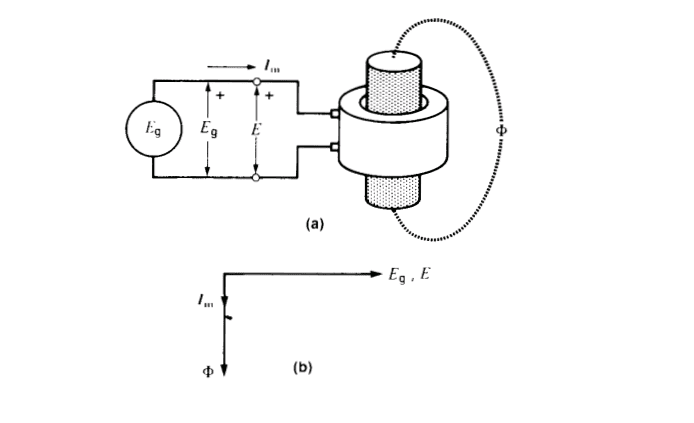
V1 is anti phase with E1?
or
in phase like this?
The phasor diagram of a no load ideal transformer is a graphical representation of the voltage and current in both the primary and secondary windings of the transformer. It shows the phase relationship between the primary and secondary voltages and currents, as well as the magnitude of these quantities.
The no load condition is important in an ideal transformer because it allows us to analyze the transformer's behavior without the influence of any load on its secondary side. This helps in understanding the transformer's internal behavior and characteristics.
In a no load ideal transformer, the secondary current is zero, and the primary current is only due to the magnetizing current. This results in the primary and secondary currents being in phase with each other, and the voltage drop across the primary and secondary windings being negligible. On the other hand, in a loaded transformer, the secondary current is not zero, and the primary and secondary currents are out of phase due to the load. This results in a different phasor diagram with a different phase relationship between the primary and secondary voltages and currents.
The phasor diagram of a no load ideal transformer tells us about the transformer's internal behavior, such as the voltage and current ratio, phase relationship between the primary and secondary quantities, and the power factor. It also helps in determining the efficiency and regulation of the transformer.
The phasor diagram of a no load ideal transformer is useful in practical applications as it helps in understanding the transformer's behavior and characteristics. It also helps in designing and analyzing the performance of transformers, such as determining the winding turns ratio and selecting the appropriate transformer for a specific application.