- #1
mickdriscoll
- 13
- 0
hi everyone,
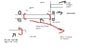
suppose i have a system of gears where one shaft contains the initial pinion. a drive torque is applied to the pinion shaft so that the pinion then applies a force to the gear its connected to. how would i calculate the forces on the gear shaft? it is a static system (contant velocity and load torque).
suppose i have a system of gears where one shaft contains the initial pinion. a drive torque is applied to the pinion shaft so that the pinion then applies a force to the gear its connected to. how would i calculate the forces on the gear shaft? it is a static system (contant velocity and load torque).