- #1
machinarium
- 12
- 0
Homework Statement
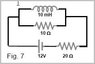
For the circuit shown in Fig. 7, what is the rate of change of the current
in the inductor when the current in the battery is 0.50 A?
(1) 600 A/s (2) 400 A/s (3) 200 A/s (4) 800 A/s (5) 500 A/s
Homework Equations
i(t)=Imax(1-e-tR/L)
induced emf = L (dI/dt)
The Attempt at a Solution
I didn't fully understand the problem. I don't understand why the current in the battery was given? What would I use that value for?
Please explain to me what I need to know to find out the rate of change of the current. Thank you very much.