- #1
scholio
- 160
- 0
Homework Statement
the capacitor is originally charged to 100 volts. the switch is closed at t=0. how long does it take for the current to drop to 0.068 amps?
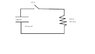
circuit drawing attached
Homework Equations
capacitance C = Q/V where Q is charge, V is electric potential
V = IR where I is current, R is resistance
I = dW/dt where W is work, t is time
I = epsilon/ R_1 + R_2 where epsilon is battery emf, R is resistance
QV/t = I^2R where t is time ---> t = QV/I^2R
The Attempt at a Solution
right now, i am trying to figure out the equation to use, i have a feeling the capacitance formula does not come into play. but there is a capacitance value given in the diagram of 100*10^-6 farads, should i use C = Q/V to find charge Q?
Q = CV = 100*10^-6 (100) = 0.01 coulombs
the variables i do have are R and V, so i can find I using I = V/R = 100/200 = 0.5 ampere
t = QV/I^2R ---> should I be the change in I (0.5 - 0.068 = 0.432)?
t = (0.01*100)/(0.068^2(200)) = 1/0.9248 = 1.08 seconds
did i do it correctly?
Attachments
Last edited: