- #1
uzair_ha91
- 92
- 0
This is so far I've learnt...potentiometer is a potential divider, it also functions to measure the unknown emf of a cell (Ex).
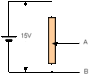
Here is the image of a potential divider:
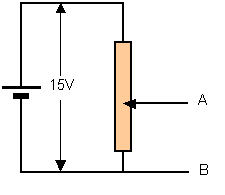
And here is one of a potentiometer:

The thing that confuses me here is that if you compare both images, you will see that the battery terminals are reversed in the next one...What would have happened if you had the circuit in image 1 and had added the unknwn emf source and galvanometer in the parallel without changing anything else? Does it make difference in the operation if you have a potential divider and you reversed the terminals of the battery?
(Hope this all makes sense to you guyz cause I'm pretty confused here)
Here is the image of a potential divider:
And here is one of a potentiometer:
The thing that confuses me here is that if you compare both images, you will see that the battery terminals are reversed in the next one...What would have happened if you had the circuit in image 1 and had added the unknwn emf source and galvanometer in the parallel without changing anything else? Does it make difference in the operation if you have a potential divider and you reversed the terminals of the battery?
(Hope this all makes sense to you guyz cause I'm pretty confused here)