- #1
ally34
- 8
- 0
Homework Statement
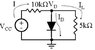
Refer to the figure attached. Let IS = 25 fA and VCC = 10V. What is the total current, the current in the diode, and the current in the 5KΩ resistor? What is VD? Use the iteration technique.
Homework Equations
Ideal Diode Equation: I = Is(e^(Vd/Vt) - 1)
Ohm's Law: V= IR
Thermal Voltage: V = kt/q = 25.9mV
The Attempt at a Solution
Total Current in the circuit = 10 V / 10kΩ = 1mA
We need to find the Vd and Id using the constant voltage model and then use the iteration method using the ideal diode equation to get closer and closer to Vd and Id using iterations.
I am not sure how to analyze the circuit using the constant diode equation. I know how to use the iteration method.
Current through the diode = Current through the 5kΩ resistor.
Please help - Any suggestions will be helpful.
Thank you!