- #1
hxluo
- 14
- 0
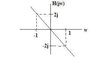
A causal LTI filter has the frequency response H(jw) shown in the graph. For each of these input signals, determine the filtered output signal y(t).
1) x(t)=exp(jt)
2) x(t)=(sin(wt))u(t)
3) X(jw)= 1 / ((jw)(6+jw))
4) X(jw)= 1 / (2+jw)
I don't understand what I have to do to find y(t), any help is appreciated, thanks
1) x(t)=exp(jt)
2) x(t)=(sin(wt))u(t)
3) X(jw)= 1 / ((jw)(6+jw))
4) X(jw)= 1 / (2+jw)
I don't understand what I have to do to find y(t), any help is appreciated, thanks