- #1
Dell
- 590
- 0
in the below question
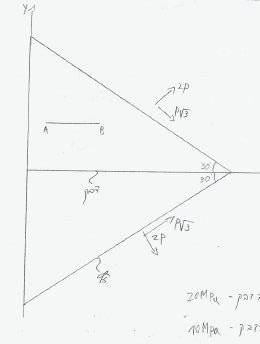
2 identical boards are glued together at their centers, the strength of the glue is 10Mpa shearing and 20Mpa normal, the strength of the boards is 10Mpa shearing and 30Mpa normal
i found the stress on the system and found
[tex]\sigma[/tex]xx= 5P
[tex]\sigma[/tex]yy= P
[tex]\sigma[/tex]xy= 0
this meaning that [tex]\theta[/tex]=0 is the principal plane and that
[tex]\sigma[/tex]s max=+-2P
now the question asks what the maximum value of P can be,
i clearly need to compare the values of the principal stresses to the strengths of the wood and glue,
my question is whether i need to compare the principal normal stress to the glues strength even though it is at 45 degrees to the plane where the glue lies??
meaning: the glue lies on the x-axis but the maximum stress is at 45 degrees so do i need to compare the normal strength at 90 degrees (P) or the maximum stress (5P)??
same goes for the shear stress?
at first i thought i just need to compare it to the stress perpindicular to the x axis, and the shear stress parallel to it, but someone told me that since the "stress cube" is tiny and the glue does have some volume, i need to compare the maximum stresses to the glues strength
therefore i would get P<=4
whereas had i not done that ii would have P<=5
2 identical boards are glued together at their centers, the strength of the glue is 10Mpa shearing and 20Mpa normal, the strength of the boards is 10Mpa shearing and 30Mpa normal
i found the stress on the system and found
[tex]\sigma[/tex]xx= 5P
[tex]\sigma[/tex]yy= P
[tex]\sigma[/tex]xy= 0
this meaning that [tex]\theta[/tex]=0 is the principal plane and that
[tex]\sigma[/tex]s max=+-2P
now the question asks what the maximum value of P can be,
i clearly need to compare the values of the principal stresses to the strengths of the wood and glue,
my question is whether i need to compare the principal normal stress to the glues strength even though it is at 45 degrees to the plane where the glue lies??
meaning: the glue lies on the x-axis but the maximum stress is at 45 degrees so do i need to compare the normal strength at 90 degrees (P) or the maximum stress (5P)??
same goes for the shear stress?
at first i thought i just need to compare it to the stress perpindicular to the x axis, and the shear stress parallel to it, but someone told me that since the "stress cube" is tiny and the glue does have some volume, i need to compare the maximum stresses to the glues strength
therefore i would get P<=4
whereas had i not done that ii would have P<=5