- #1
An1MuS
- 38
- 0
I'm working on a group project where we test a bicycle frame on ABAQUS.
The test is as follow
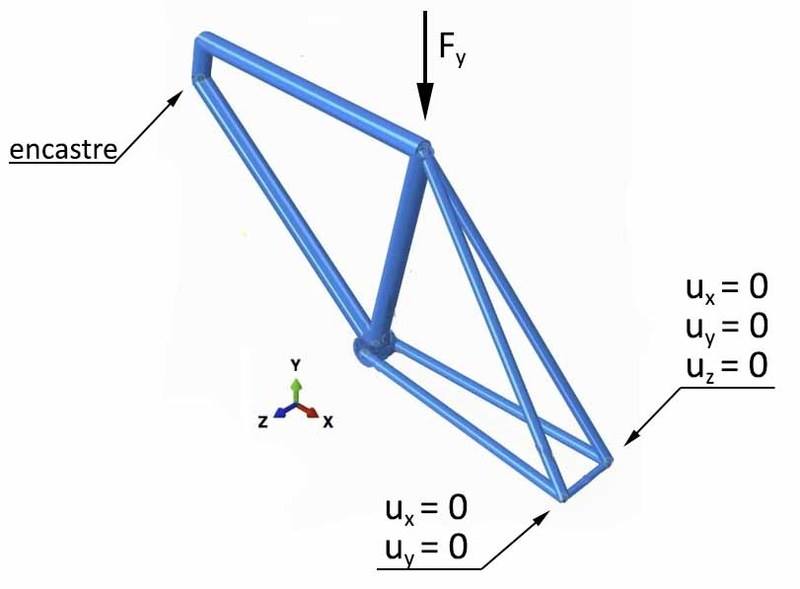
Where F is a static load. It was suggested for us to consider it as 4G*120kg to simulate a laboratory test. We're having a hard time knowing what is the maximum deflection (or stifness) we should allow.
I can't find any tests like this, or websites where i could get that information. Does anyone have any idea?
The test is as follow
Where F is a static load. It was suggested for us to consider it as 4G*120kg to simulate a laboratory test. We're having a hard time knowing what is the maximum deflection (or stifness) we should allow.
I can't find any tests like this, or websites where i could get that information. Does anyone have any idea?