- #1
utkarshakash
Gold Member
- 854
- 13
Homework Statement
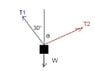
A heavy box weighing 25kN is to be lifted by 2 overhead cranes with cables inclined at 40° and 30° with the vertical respectively.
i) Find tension in each cable during lifting.
ii) Due to safety concerns, the tension T2 in second cable is to be minimized. Find the angle of inclination of this cable for this purpose.
Homework Equations
Lami's Theorem
The Attempt at a Solution
I'm mainly concerned with the second part of the question. Applying Lami's Theorem, I can easily find the answer to the first part. I'm sure there exists a geometrical method for the second part but I'm not sure how to start. What about triangle inequalities? Will it be of any help?