- #1
nothingsus
- 16
- 0
Homework Statement
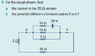
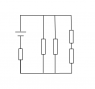
In the circuit shown, find the current in the 20-ohm resistor and the potential difference between points X and Y.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I've never really ran into a problem where the battery is in the parallel branches with resistors. The voltage drop of the parallel branch surely can't be 25V otherwise there would no voltage drop over the other resistors which are in series.
I am quite lost with this question. Could someone please explain in full how they got their answer?
Thanks.
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: