- #1
chevinbrown
- 2
- 0
Gear Clamp Design--Describe Friction Force
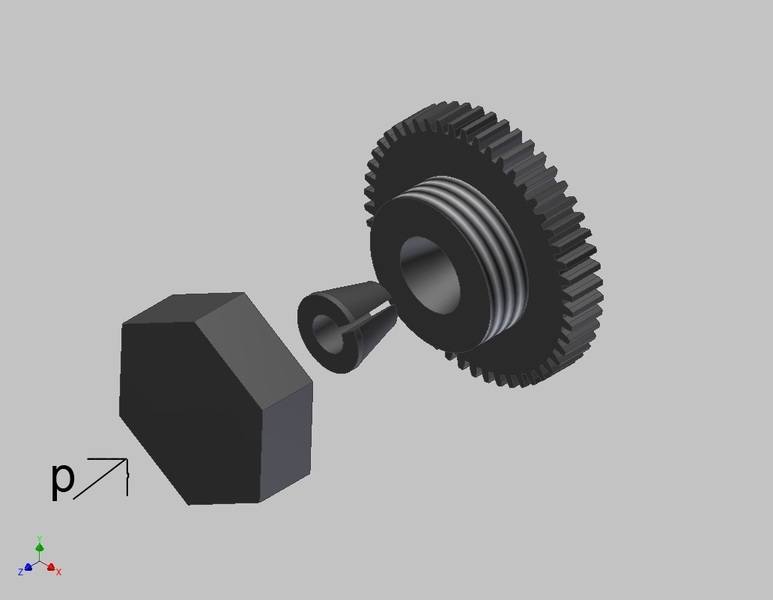
I need to know how much frictional force is exerted on both sides of the collet (the piece in the middle of the image) when a force 'p' is applied by the cap nut.
(See attachment)
This is my first post here. Let me
 know if I'm being too vague. :)
know if I'm being too vague. :)
I need to know how much frictional force is exerted on both sides of the collet (the piece in the middle of the image) when a force 'p' is applied by the cap nut.
(See attachment)
This is my first post here. Let me
Attachments
Last edited: