- #1
sweetdreams12
- 9
- 0
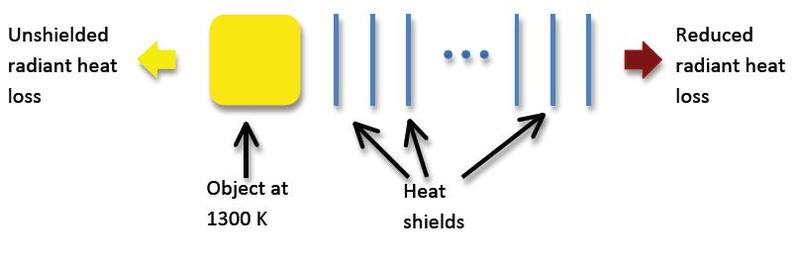
A “blackbody heat shield” is used to reduce radiant heat loss in situations where standard low conductivity insulation (i.e. normal insulation) cannot be used. The shield is constructed using a set of parallel metal sheets, each with emissivity 1.0.
Explain how/why this “heat shield” works and determine how many sheets of metal are
required to reduce the heat loss to less than 20% of the unshielded value. (Hint: think
about the radiation absorbed by each sheet and how this energy will be re-radiated.)
Diagram:
I really need help with this xD I don't even know where to begin.
Explain how/why this “heat shield” works and determine how many sheets of metal are
required to reduce the heat loss to less than 20% of the unshielded value. (Hint: think
about the radiation absorbed by each sheet and how this energy will be re-radiated.)
Diagram:
I really need help with this xD I don't even know where to begin.