- #1
tigert2004
- 9
- 0
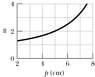
An object is moved along the central axis of a spherical mirror while the lateral magnification m of it is measured. Figure 34-32 gives m versus object distance p for a range of p. What is the magnification of the object when the object is 36 cm from the mirror?
I understand that m=-i/p but we don't have i so I looked at the graph and i changes exponetially?
some points on the graph (4,1.75) i=7
(5,2) i=10
(6,2.5) i=15
(7,3.125) i=21.9
I don't see where this is going
I understand that m=-i/p but we don't have i so I looked at the graph and i changes exponetially?
some points on the graph (4,1.75) i=7
(5,2) i=10
(6,2.5) i=15
(7,3.125) i=21.9
I don't see where this is going