- #1
Aureum
- 5
- 0
I understand relative length well but I what to image a 3d object traveling close to the speed of light. As we know objects have speed, direction, and rotation. So I was wondering if there is a general equation to calculate the relative volume change of a Rectangular Prism rotating and traveling near the speed of light at any given time.
Relevant equations
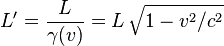
Relevant equations