- #1
aychamo
- 375
- 0
Hi,
I'm having a brain fart. Consider the amino acid glutamate (glutamic acid):
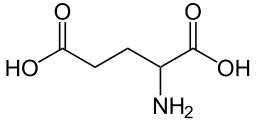
->
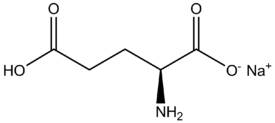
When it forms an ionic bond with Na+ to make MSG, the glutamic acid loses it's hydrogen on the right side. Is it that it was "oxidized"? Or what do we call the process where it loses the hydrogen and is then able to form an ionic bond? And what is the driving force for this reaction?
I'm having a brain fart. Consider the amino acid glutamate (glutamic acid):
->
When it forms an ionic bond with Na+ to make MSG, the glutamic acid loses it's hydrogen on the right side. Is it that it was "oxidized"? Or what do we call the process where it loses the hydrogen and is then able to form an ionic bond? And what is the driving force for this reaction?