- #1
ultrauser
- 23
- 0
If I understand it correct during hammerthrow an athlete muscles cause Fcentripetal force on a ball and ball cause reaction Fcentrifual force on athlete.
The athlete also cause Frotation on ball by rotating his body and ball cause Freaction on athlete.
What would happen if athlete would try to throw the heavier ball than himself being in the air - by rotating his body (no friction between athlete and the Earth - I mean the athlete and the ball are both in the air) ? Would it be even possible or would athlete rotate himself around ball(cause ball is heavier) ?
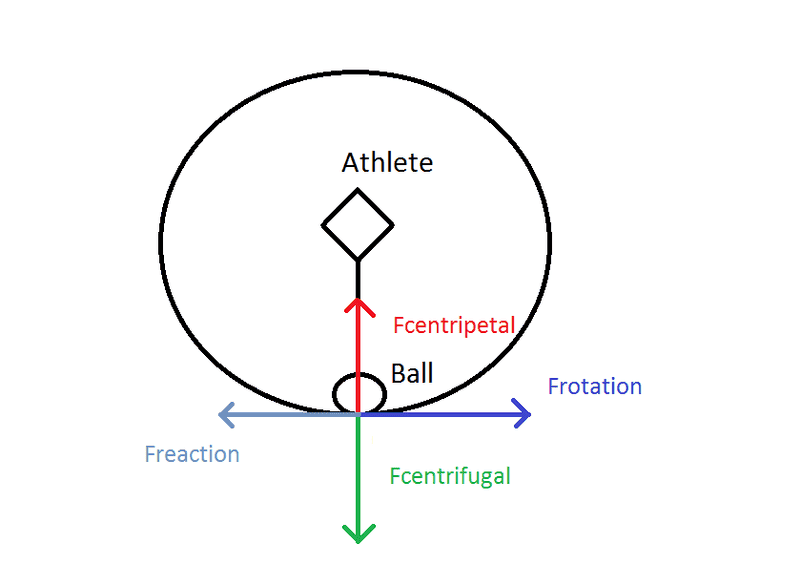
The athlete also cause Frotation on ball by rotating his body and ball cause Freaction on athlete.
What would happen if athlete would try to throw the heavier ball than himself being in the air - by rotating his body (no friction between athlete and the Earth - I mean the athlete and the ball are both in the air) ? Would it be even possible or would athlete rotate himself around ball(cause ball is heavier) ?