- #1
anhnha
- 181
- 1
I am reading about Boost-Flyback converter and this is a bit confusing.
Could you explain the role of D1 and C1 here?
The lecture says that "D1 and C1deliver to the output the energy stored in the transformer leakage inductance Ld." I can't understand what is meant here.
And could you explain why there is Lm there?
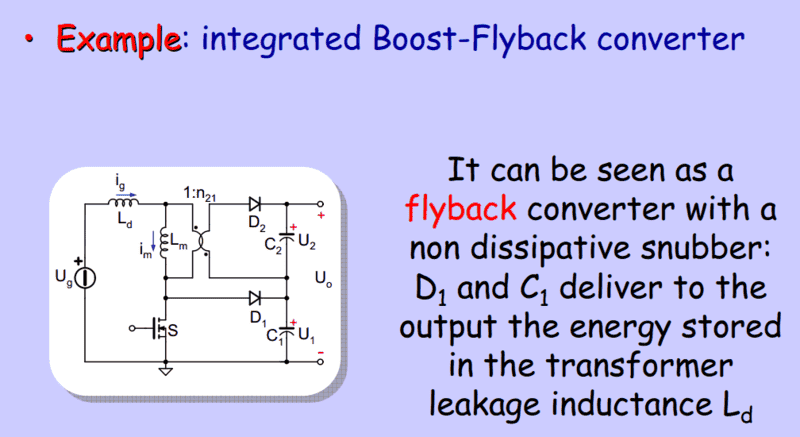
Could you explain the role of D1 and C1 here?
The lecture says that "D1 and C1deliver to the output the energy stored in the transformer leakage inductance Ld." I can't understand what is meant here.
And could you explain why there is Lm there?
