- #1
ABhattacharya
- 2
- 0
Hello, a newbie here. I need to understand the relationship between MO and Energy Bands.
Although i have searched and researched about this topic in Google, but i am yet to understand this part clearly.
It is said that Energy Bands occur as the number of MO increase due to the various atoms that are interlinked in a crystal structure.
But i can't help but wonder.
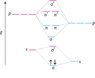
While K has its σ state fully filled and its σ* state empty, and yet behaves as a conductor
But Si has ∏px and ∏py states partially filled which means when bands form, Si should have some bands which are partially filled and hence should be good conductors while Na should behave more of a semiconductor way... but it is just the opposite. Why?
Although i have searched and researched about this topic in Google, but i am yet to understand this part clearly.
It is said that Energy Bands occur as the number of MO increase due to the various atoms that are interlinked in a crystal structure.
But i can't help but wonder.
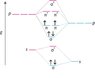
While K has its σ state fully filled and its σ* state empty, and yet behaves as a conductor
But Si has ∏px and ∏py states partially filled which means when bands form, Si should have some bands which are partially filled and hence should be good conductors while Na should behave more of a semiconductor way... but it is just the opposite. Why?