- #1
kooombaya
- 36
- 0
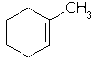
Using this reference as an example let's name the double bonded carbon attached to the methyl as C1. In my textbook it says that C1 has two alkyl groups on it. The CH3 is one alkyl group and the carbon to the left of C1 is the other alkyl group (let's call this C2). I'm confused, why is C2 considered to be an alkyl group?