- #1
lmkjason
- 2
- 0
Ammeter to help the circuit work!
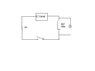
I have connected one IC circuit which is taking from a remote control car. Then I connect it to the a power supply which is 9V. It doesn't work in the beginning. But I don't know why it works after I connect an ammeter in parallel to the resistor which in in series to the motor. The circuit diagram is attached. I have tried to use a variable resistor to instead of the 4k7 ohm resistor and remove the ammeter. But the circuit doesn't work. Do I need to use a capacitor to stablize the current flow into the motor. Or I need to add another amplifier to increase the current input into the motor. But I think it is quite dangerrous to add a amplifier directly in series with the motor since it may burst. Also, do I need to add an inductor to store the energy. Thank you for any help for that.
I have connected one IC circuit which is taking from a remote control car. Then I connect it to the a power supply which is 9V. It doesn't work in the beginning. But I don't know why it works after I connect an ammeter in parallel to the resistor which in in series to the motor. The circuit diagram is attached. I have tried to use a variable resistor to instead of the 4k7 ohm resistor and remove the ammeter. But the circuit doesn't work. Do I need to use a capacitor to stablize the current flow into the motor. Or I need to add another amplifier to increase the current input into the motor. But I think it is quite dangerrous to add a amplifier directly in series with the motor since it may burst. Also, do I need to add an inductor to store the energy. Thank you for any help for that.