- #1
kishlaysingh04
- 5
- 0
Homework Statement
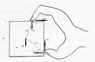
a square box held with a person's fingers pushing downward one quarter of the way along the top of the box and with their thumb pushing side wards on the bottom of the side face of the box. Friction between the person's fingers and the box is obviously very important if the box is not to fall.Determine the required coefficient of friction to keep the box from falling.
θ=tan-1 (1/2) and α= 45°
2. The attempt at a solution
I have drawn he following forces to show you
the equations which i have got is:
μN2= N2 + Mg
and by balancing the torque I have got :
N2 x root 5a x sinθ = μN2 x 2 root 2 x cosα[