- #1
Modrisco
- 8
- 0
I've asked this question about 4 times on yahoo but no one seems to have the brains to answer it!
Looking at the diagram:
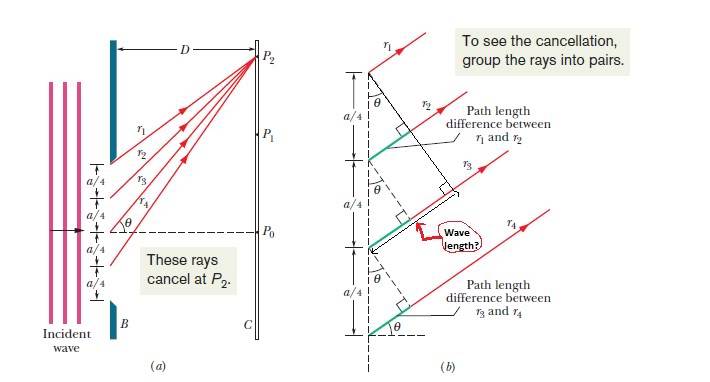
Just trying to get a better understand of "λ = asin Ѳ"
I've marked what I think is the wavelength...can someone please advise? as I'm trying to get a report done and I don't want to say the wrong thing!
If that's not the wavelength..is it the green line?
Thank you!
Looking at the diagram:
Just trying to get a better understand of "λ = asin Ѳ"
I've marked what I think is the wavelength...can someone please advise? as I'm trying to get a report done and I don't want to say the wrong thing!
If that's not the wavelength..is it the green line?
Thank you!