- #1
Siune
- 24
- 0
Hello, just been reading a little bit about the basics of moving coil meter and one thing is bugging me.
First if we have a basic square looped coil in and uniform magnetic field. There is torque ( m x B ) due to the magnetic field and then there is the system/spring attached to the coil which gives the opposing torque ( cθ ).
So in the end we get that the current in the coil is:
[itex] I = \frac{c}{BA} \frac{\phi}{cos(\phi)}[/itex]
Cleary the I is very non-linear as function of phi as the surface of the coil makes angle with the magnetic field ( Which is uniform ).
Now we have d'Arsonval galvanometer, like in the picture:
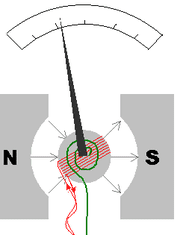
Now the magnetic field is clearly not uniform as the "iron core" sucks in the magnetic field. The field between the poles and the iron core becomes radial. Now it says that the surface area vector of the plane of the loop (n or m if we talk about dipole ) is always perpendicular to the magnetic field. I can't really figure it out as the magnetic field inside is uniform ( horizontal ) inside the soft iron core.
I can understand that the coil is wounded around the iron core so we should compare the field to the outside field ( radial ) but as we compare the angle with the normal vector of the surface of the loop and the magnetic field so. :l
The page is 424, in Understanding Physics, Mansfield & O'Sullivan (Second edition).
http://books.google.fi/books?id=19TCz0cxAFMC&printsec=frontcover&hl=fi#v=onepage&q&f=false
First if we have a basic square looped coil in and uniform magnetic field. There is torque ( m x B ) due to the magnetic field and then there is the system/spring attached to the coil which gives the opposing torque ( cθ ).
So in the end we get that the current in the coil is:
[itex] I = \frac{c}{BA} \frac{\phi}{cos(\phi)}[/itex]
Cleary the I is very non-linear as function of phi as the surface of the coil makes angle with the magnetic field ( Which is uniform ).
Now we have d'Arsonval galvanometer, like in the picture:
Now the magnetic field is clearly not uniform as the "iron core" sucks in the magnetic field. The field between the poles and the iron core becomes radial. Now it says that the surface area vector of the plane of the loop (n or m if we talk about dipole ) is always perpendicular to the magnetic field. I can't really figure it out as the magnetic field inside is uniform ( horizontal ) inside the soft iron core.
I can understand that the coil is wounded around the iron core so we should compare the field to the outside field ( radial ) but as we compare the angle with the normal vector of the surface of the loop and the magnetic field so. :l
The page is 424, in Understanding Physics, Mansfield & O'Sullivan (Second edition).
http://books.google.fi/books?id=19TCz0cxAFMC&printsec=frontcover&hl=fi#v=onepage&q&f=false