- #1
NUKE1989
- 1
- 0
Hi all. I am new here but i decided to work a bit more and finish my diploma faster so i think i will use this forum more from now on.
I was studing about quark color changes, quark interactions, gluons and generally the strong force. As i saw the Feynman diagrams i felt a bit confused.
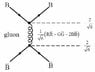
What are the laws in order to know which gluon is emmited each time? For example in my first pic why is this a green-antiblue gluon and not a blue-antigreen?
In the second picture how do i know its 1/√6(RR+GG-2BB) and not 1/√2 (RR+BB) for example?
And in the knots again how do i found those numbers?
Thanks for your time!
I was studing about quark color changes, quark interactions, gluons and generally the strong force. As i saw the Feynman diagrams i felt a bit confused.
What are the laws in order to know which gluon is emmited each time? For example in my first pic why is this a green-antiblue gluon and not a blue-antigreen?
In the second picture how do i know its 1/√6(RR+GG-2BB) and not 1/√2 (RR+BB) for example?
And in the knots again how do i found those numbers?
Thanks for your time!