- #1
bhaazee
- 80
- 0
Consider a rotor rotating inside a stator. The rotating torque produces a moment. This moment will be counter balanced by generating a counter- torque (by rotating the stator or some other element in counter direction).
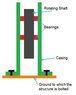
Now, my query is that I have a pump rotating a considerable mass and this mass is supported by two bearings. The casing in which this mass is enclosed has to be bolted to a fixed support. This means, the bolts are about to encounter a moment due to rotation. I want to know, if this moment encountered by the bolts are equal to the moment developed by the rotating mass or will it be lower (means the moment only due to friction co-efficient of bearings)?
Regards.
Now, my query is that I have a pump rotating a considerable mass and this mass is supported by two bearings. The casing in which this mass is enclosed has to be bolted to a fixed support. This means, the bolts are about to encounter a moment due to rotation. I want to know, if this moment encountered by the bolts are equal to the moment developed by the rotating mass or will it be lower (means the moment only due to friction co-efficient of bearings)?
Regards.