- #1
bjm5295
- 1
- 0
If anyone can help me out, i'd really appreciate it. I'm not necessarily looking for the answer, but more how to get to the answer. Thank alot.
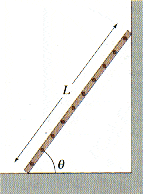
A uniform ladder of mass m and length L leans at an angle
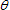 against a frictionless wall, Fig. 9-61. If the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is 0.43, what is the minimum angle at which the ladder will not slip?
against a frictionless wall, Fig. 9-61. If the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is 0.43, what is the minimum angle at which the ladder will not slip?
P.S. Whats theta mean? =X For whatever reason I never learned what it means in Physics 1.
A uniform ladder of mass m and length L leans at an angle
P.S. Whats theta mean? =X For whatever reason I never learned what it means in Physics 1.
Last edited by a moderator: