- #1
Zencapop
- 2
- 0
Ok,
Here is a problem that I have been thinking about. Let me know what you guys think its going to look like.
For this problem, we assume that faster than light speed travel is possible and that we have a telescope that can see a spaceship 1 light year away.
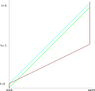
Imagine that a spaceship comes and docks 1 light-year away from Earth. It stays there for about 5 minutes, and then travels at 2 times the speed of light, reaching Earth in 6 months. It then stays docked on Earth for 6 more months.
My question is, what will the journey look like from Earth? It should be strange because the light from the ship when it initially docked would reach Earth 1 year later. But the ship would already be on Earth after 6 months. After a year, will we see two ships for five minutes, one docked on Earth and one docked 1 light year away? What will the movement of the ship look like after a year, as it would have started moving then, at least the movement from its light would start reaching us. But, the ship would have already started becoming visible much earlier, as it was traveling towards us.
Its mind boggling, isn't it?
Here is a problem that I have been thinking about. Let me know what you guys think its going to look like.
For this problem, we assume that faster than light speed travel is possible and that we have a telescope that can see a spaceship 1 light year away.
Imagine that a spaceship comes and docks 1 light-year away from Earth. It stays there for about 5 minutes, and then travels at 2 times the speed of light, reaching Earth in 6 months. It then stays docked on Earth for 6 more months.
My question is, what will the journey look like from Earth? It should be strange because the light from the ship when it initially docked would reach Earth 1 year later. But the ship would already be on Earth after 6 months. After a year, will we see two ships for five minutes, one docked on Earth and one docked 1 light year away? What will the movement of the ship look like after a year, as it would have started moving then, at least the movement from its light would start reaching us. But, the ship would have already started becoming visible much earlier, as it was traveling towards us.
Its mind boggling, isn't it?