- #1
sathishlmw
- 3
- 0
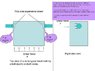
I am trying to understand the behavior of bolt in different
plane.
My doubt is when shear force acts on bolts in 2 different
plane simultaneously, does it share the shear force (F/2) or
each bolts experience the total force (F).
I am sure that if there is a bolt pattern on the same plane,
each bolt will contribute (develop individual reaction shear force).
Please find the attachment.
plane.
My doubt is when shear force acts on bolts in 2 different
plane simultaneously, does it share the shear force (F/2) or
each bolts experience the total force (F).
I am sure that if there is a bolt pattern on the same plane,
each bolt will contribute (develop individual reaction shear force).
Please find the attachment.