- #1
Pellefant
- 37
- 0
The source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/E_(mathematical_constant)
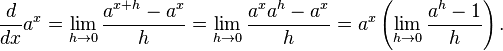
I can not understand the last peace in that equation,
If e=a it will be e^x*((1-1)/0) ...which means 0/0, that don't make sense :(, what am i missing
I can not understand the last peace in that equation,
If e=a it will be e^x*((1-1)/0) ...which means 0/0, that don't make sense :(, what am i missing