- #1
r_swayze
- 66
- 0
[tex]
\int_0^1\int_0^y e^{x^2} dx dy
[/tex]
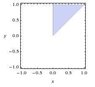
The region I am integrating over should look like this graph, right?
I tried switching the bounds but I am left where what I started.
since 0 < x < y, and 0 < y < 1
I can switch to 0 < x < 1 , and x < y < 1
leaving me with the integral [tex]
\int_0^1\int_x^1 e^{x^2} dy dx
[/tex]
integrating gives ex2y
then substituting the values for y gives [tex]
\int_0^1 e^{x^2} - e^{x^2}x dx
[/tex]
Am I integrating over the wrong bounds? I know if 0 < y < x, it would work.
\int_0^1\int_0^y e^{x^2} dx dy
[/tex]
The region I am integrating over should look like this graph, right?
I tried switching the bounds but I am left where what I started.
since 0 < x < y, and 0 < y < 1
I can switch to 0 < x < 1 , and x < y < 1
leaving me with the integral [tex]
\int_0^1\int_x^1 e^{x^2} dy dx
[/tex]
integrating gives ex2y
then substituting the values for y gives [tex]
\int_0^1 e^{x^2} - e^{x^2}x dx
[/tex]
Am I integrating over the wrong bounds? I know if 0 < y < x, it would work.