- #1
zeroktrian
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement
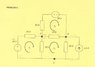
Using mesh analysis work out the currents flow through each of the three meshes. From these current values calculate the voltage of node A, and node B with respect to the ground node.
Find equivalents of sub circuits A-G, B-G, A-B by applying Thevenin's theory. Then place these equivalents together and prove that the voltage at node A, and node B will be the same as in the previous problem.
Homework Equations
Kirchhoff's Current and Voltage Laws, Thevenin's laws.
The Attempt at a Solution
My attempt at the solution should be visible in the images I uploaded. The three current values I obtained through Mesh Analysis have been verified using the Circuit Wizard program. My only uncertainties are with regards to determining the voltages at node A and B with respect to the ground node.
I am not certain whether my method for their determination using the currents from the Mesh Analysis are correct. Also, with their verification using Thevenin's theorem, I am not certain about how exactly to figure out the node voltages using the theorem.
If anyone could guide me in the right direction I would be most appreciative.
Thanks.