- #1
Matriculator
- 51
- 0
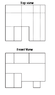
I'm having a hard time envisioning what the orthogonal view of this object in 3-D. It is mainly because of the continuous surface on the front view. Is that way in the back and the there are rectangular blocks sticking out? Thank you. I would have an easier time if a right view was included but there are the only two views.