- #1
DivGradCurl
- 372
- 0
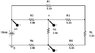
I have a simple question about AC/DC. I expected a circuit with a given DC voltage to be equivalent to one with an AC voltage whose value (peak-to-peak) is the same (at least theoretically). For 10 V DC, I get a load voltage of 1.6667 V, whereas 10 Vp-p AC gives 1.6602 V (simulation). Are there theoretical grounds behind this result? Since my simulation was run under ideal conditions, I think I should get the same result, but it's not the case. I would like to understand why. By the way, snapshots of the circuits are attached.
Any help is highly appreciated.
NOTE: THE PROBES USED IN MY SIMULATION ARE ACROSS THE "RL" ONLY (NOT EXACTLY AS SHOWN IN THE FIGURES)
Any help is highly appreciated.
NOTE: THE PROBES USED IN MY SIMULATION ARE ACROSS THE "RL" ONLY (NOT EXACTLY AS SHOWN IN THE FIGURES)