- #1
e.pramudita
- 14
- 0
QUESTION
Rainwater collects behind the concrete retaining wall shown in the figure. If the water saturated soil (specific gravity 2.2) acts as a fluid, determine the force and center of pressure on a 1-m width of the wall.
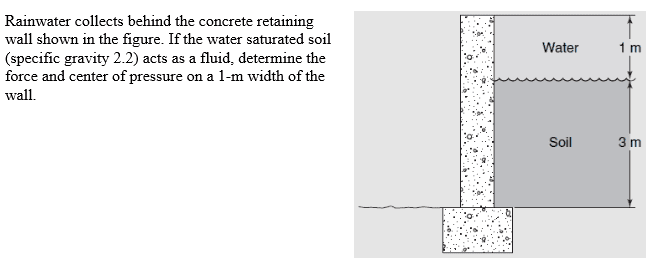
PROBLEM
1. What does it mean by 1-m width of the wall? Is it 1-m from contact surface with water and soil? Isn't the value of force depends on the height (since pressure does)?
2. [tex] dF=P_G ~dA [/tex] is the definition of force. How can I apply this for 1-m, 2-m, 3-m, or x-m width of the wall?
It is essentially asking for the force value inside the wall vertically. But shouldn't this value depends on the height (y) since pressure does?
P.S. How do you make mathematics symbols in the same line with usual word. If I were to write latex here [tex] like this [/tex] it makes a new line.
Rainwater collects behind the concrete retaining wall shown in the figure. If the water saturated soil (specific gravity 2.2) acts as a fluid, determine the force and center of pressure on a 1-m width of the wall.
PROBLEM
1. What does it mean by 1-m width of the wall? Is it 1-m from contact surface with water and soil? Isn't the value of force depends on the height (since pressure does)?
2. [tex] dF=P_G ~dA [/tex] is the definition of force. How can I apply this for 1-m, 2-m, 3-m, or x-m width of the wall?
It is essentially asking for the force value inside the wall vertically. But shouldn't this value depends on the height (y) since pressure does?
P.S. How do you make mathematics symbols in the same line with usual word. If I were to write latex here [tex] like this [/tex] it makes a new line.