- #1
ionlylooklazy
- 30
- 0
i've always been a little confused on transfer functions, could someone offer me some tips/hints please?
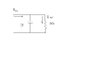
if I have this circuit shown,
a transfer function is the ratio of the input to the output?
can it be the ratio of the currents, or must it be the voltages, also, in this circuit, would the input be considered across the capacitor?
if I have this circuit shown,
a transfer function is the ratio of the input to the output?
can it be the ratio of the currents, or must it be the voltages, also, in this circuit, would the input be considered across the capacitor?