- #1
Saladsamurai
- 3,020
- 7
Hello all 
I am trying to sort out how to use pass by reference properly and I am getting a Build error related to my pass by reference function. Perhaps someone could help me out here. I thought I was doing this correctly by reading my text, but apparently not. Maybe someone can point out if I am missing the obvious here:
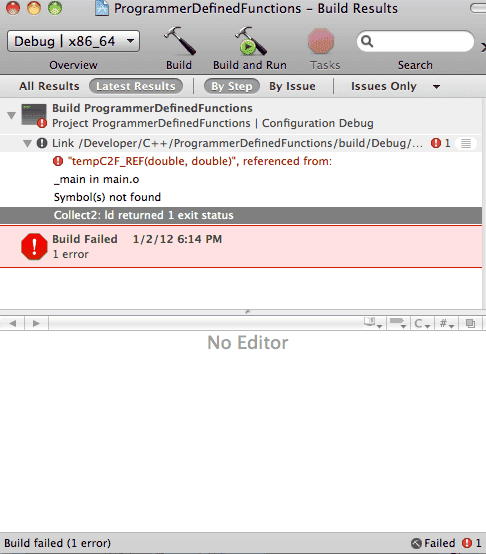
Here is the build error I am getting:
Here is a sample input file:
I am trying to sort out how to use pass by reference properly and I am getting a Build error related to my pass by reference function. Perhaps someone could help me out here. I thought I was doing this correctly by reading my text, but apparently not. Maybe someone can point out if I am missing the obvious here:
Code:
/*----------------------------------------------------
Examples of some simple programmer-defined functions
The 'main ()' function will make calls to 2 programmer
defined functions: 1) that will be simple PASS BY VALUE
which is the C++ default and 2) a PASS BY REFERENCE that
is used to change the value of a function parameter. The
functions will operate on values in a .txt file named
input.txt and will send output to a file named
output.txt ... how clever ...
----------------------------------------------------*/
#include <iostream> // required for cin, cout, cerr
#include <fstream> // required for ifstream, ofstream
#include <iomanip> // required for setw
using namespace std;
// function prototypes
double tempC2F_VAL(double tempInCelsius);
void tempC2F_REF(double tempInCelsius, double returnByREF);
// main program
int main ()
{
// declare variables in scope of main()
double TVal, TRef(0), tempC;
ifstream fin;
ofstream fout;
// bind fin to input.txt
fin.open("input.txt");
// make sure fin opened properly
if (!fin)
{
cerr << "Could not open input file ... \n";
}
//open output file
fout.open("output.txt");
// print header
fout << setw(5) << "Celsius"
<< setw(20) << "F-Pass by VALUE"
<< setw(25) << "F-Pass by REF"
<< endl;
while (!fin.eof())
{
// read in values and convert
fin >> tempC;
// PASS BY VALUE CONVERSION
TVal = tempC2F_VAL(tempC);
// PASS BY REFERENCE CONVERSION
tempC2F_REF(tempC, TRef);
fout << setw(5) << tempC
<< setw(20) << TVal
<< setw(25) << TRef
<< endl;
}
// close all files and exit
fin.close();
fout.close();
return 0;
}
/*----------------------------------------------------
1) A PASS BY VALUE function
Converts temperature in Celsius to Fahrenheit
Precondition: tempC holds temp in Celsius
Postcondition: returns temp in Fahrenheit
----------------------------------------------------*/
double tempC2F_VAL(double tempC) //function header
{
// declare local variables
double tempF;
// convert
tempF = tempC *(9.0/5.0) + 32.0;
// return value in Fahrenheit
return tempF;
}
/*----------------------------------------------------
2) A PASS BY REFERENCE function
Converts temperature in Celsius to Fahrenheit
Precondition: tempC holds temp in Celsius
Postcondition: value of TRef in main() has been updated
Note that function return is of type 'void' since it
doe not 'return' anything. It augments TVal directly
----------------------------------------------------*/
void tempC2F_REF(double tempC, double& TRef) //function header
{
// convert
TRef = tempC *(9.0/5.0) + 32.0;
return;
}Here is the build error I am getting:
Here is a sample input file:
Code:
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50