- #1
jean28
- 85
- 0
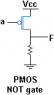
Hey guys. I am simply trying to derive the equation for Vout in a PMOS inverter (attached). I know that in an NMOS inverter (which has the resistor in top of the transistor instead of the bottom) the equation for Vout is:
Vdd - id*rd.
But how does the resistor being in the bottom change this behavior? Is it now Vcc - ground? (which would equal Vcc).
Thanks.
Vdd - id*rd.
But how does the resistor being in the bottom change this behavior? Is it now Vcc - ground? (which would equal Vcc).
Thanks.