- #1
Lunat1c
- 66
- 0
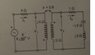
For the circuit attached, I'm first asked to find [tex] I_1, I_2, V_1, V_2 [/tex] by using the appropriate loop equations. I got these answers (which I checked and are correct):
[tex] \overline{I_1} = 1.556A\angle61.4^\circ [/tex]
[tex] \overline{I_2} = 1.111A\angle-100.25^\circ [/tex]
[tex] \overline{V_1} = 3.92V\angle139.8^\circ [/tex]
[tex] \overline{V_2} = 1.57V\angle-55.25^\circ [/tex]
My questions are these:
1. I got the value of V2 by multiplying I2 with (1 - j2 + j3). Why on Earth don't I get the same answer if I use the fact that [tex] V_2 = I_{2}j2 + I_{1}X_{m} [/tex]
Where Xm is the impedance as a result of the mutual inductance which I calculated using [tex] X_m = k\sqrt{j4 * j2} [/tex].
Also, shouldn't V2 be a stepped up/down version of V1 but phase shifted by 180 degrees? (from the dot convention)
2. How can I obtain the same results using the reflected impedance concept? Without knowing the turns ratio I can't do this and I can't seem to be able to find a way to find the turns ratio by using the coupling coefficient 'k' or any other of the known data. A hint would be much appreciated.
Thank you in advance for any help you can offer!
[tex] \overline{I_1} = 1.556A\angle61.4^\circ [/tex]
[tex] \overline{I_2} = 1.111A\angle-100.25^\circ [/tex]
[tex] \overline{V_1} = 3.92V\angle139.8^\circ [/tex]
[tex] \overline{V_2} = 1.57V\angle-55.25^\circ [/tex]
My questions are these:
1. I got the value of V2 by multiplying I2 with (1 - j2 + j3). Why on Earth don't I get the same answer if I use the fact that [tex] V_2 = I_{2}j2 + I_{1}X_{m} [/tex]
Where Xm is the impedance as a result of the mutual inductance which I calculated using [tex] X_m = k\sqrt{j4 * j2} [/tex].
Also, shouldn't V2 be a stepped up/down version of V1 but phase shifted by 180 degrees? (from the dot convention)
2. How can I obtain the same results using the reflected impedance concept? Without knowing the turns ratio I can't do this and I can't seem to be able to find a way to find the turns ratio by using the coupling coefficient 'k' or any other of the known data. A hint would be much appreciated.
Thank you in advance for any help you can offer!
Attachments
Last edited: