- #1
KingNothing
- 882
- 4
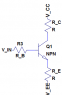
I'm confused about how exactly the output resistance and other resistances are set up in the small signal model. Is this small signal model correct? Please regard underscores as a subscript. Is r_0 always connected between collector and emitter?