- #1
fbgiant
- 4
- 0
When potentiometer is used to measure and compare emf of cells, how that balncing point is reached?...
this is the circuit diagram what i mentioned..
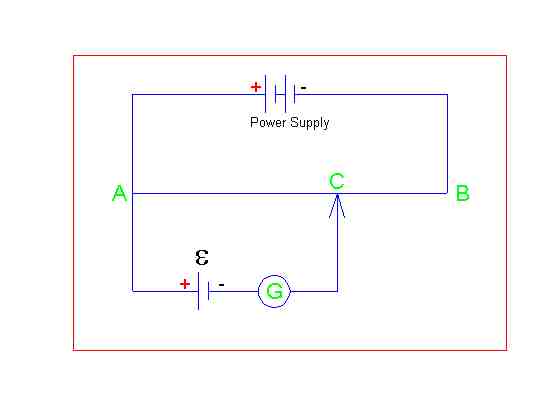
in the description it is said that at that balancing point (current through that galvanometer shows zero), potential drop across AC is equal to E emf of the cell.
But my doubt is that " by Kirchoff's voltage rule , consider that loop A-G-C-A, potential drop across AC is equal to E without any conditions like balanced or not. Then we have to say that each and every point is a balanced point, right?"
this is the circuit diagram what i mentioned..
in the description it is said that at that balancing point (current through that galvanometer shows zero), potential drop across AC is equal to E emf of the cell.
But my doubt is that " by Kirchoff's voltage rule , consider that loop A-G-C-A, potential drop across AC is equal to E without any conditions like balanced or not. Then we have to say that each and every point is a balanced point, right?"