- #1
Aziza
- 190
- 1
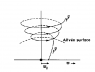
Could someone please explain exactly how the omega effect works? It is supposed to explain how a poloidal magnetic field (of the sun for example, or a black hole accretion disk) becomes toroidal. This is supposed to be due to differential rotation and the inertia of mass. But I just don't see how this can cause field lines to twist into helix...if anyone knows a good reference regarding this subject I would appreciate it, I can't find anything detailed!