- #1
stunner5000pt
- 1,461
- 2
Homework Statement
Griffith's Problem 4.18
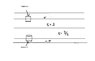
The space between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor (in the figure) is filled
with two slabs of linear dielectric material. Each slab has thickness a, so the total distance between the plates is 2a. Slab 1 has a dielectric constant of 2, and slab 2 has a dielectric constant of 1.5. The free charge density on the top plate is sigma and on the bottom plate -sigma.Find the electric displacement D in each slab.
Homework Equations
Gauss law for dielectrics
[tex] \int D \cdot dA = Q_{f,enc} [/tex]
The Attempt at a Solution
In the diagram i have posted, the top and bottom 'gaps' are the metal slabs that make up this capacitor.
For the electric displacement in the top slab where epsilon = 2
The free charge on the upper boundary of this slab is +sigma. But there is some charge going to be present within the slab as well... but that's bound charge right... so we need not worry?
The electric displacement is just +sigma for this slab. but what is the direction? I am tempted to say that it points downward because it only seems natural (positive to negative) but what if there were no negative charge involved in the question? What then?
What if in the question the bottom slab was of some charge +sigma? The free charge on the top slab is still sigma but would the direction of D be pointing downward?
Thanks for your help and input.