- #1
Outrageous
- 374
- 0
BJT ,the output voltage is amplified because there is dc voltage supply to keep BJT active ,but what about the FET? The voltage supplied only control the gate only, anything to do with the output?
Thanks
Thanks
vk6kro said:FET amplifiers also get a power supply to the output.
In a typical amplifier, the FET is placed in series with a resistor across the supply voltage.
The resistance of the FET is then varied by controlling the gate voltage and this causes the voltage across the FET to change. It behaves as part of a voltage divider where it is varying in resistance.
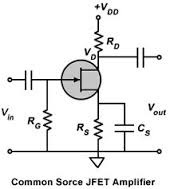
An FET (Field Effect Transistor) amplifier works by using an FET as the amplifying element. The FET controls the flow of current between the source and drain regions by varying the voltage applied to the gate. This allows the amplifier to amplify weak input signals to a larger output signal.
There are three main types of FET amplifiers: common source, common drain, and common gate. A common source amplifier has the input signal applied to the gate and the output taken from the drain. A common drain amplifier has the input signal applied to the gate and the output taken from the source. A common gate amplifier has the input signal applied to the source and the output taken from the drain.
An FET amplifier differs from a BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) amplifier in the way it controls the flow of current. FETs use voltage to control current, while BJTs use current to control current. This makes FET amplifiers better suited for high-frequency applications, as they have a faster response time.
There are several advantages of using an FET amplifier. They have a high input impedance, which means they do not load the input signal and can be used in high impedance circuits. They also have a low output impedance, which allows them to drive low impedance loads. FET amplifiers also have a wide bandwidth, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Choosing the right FET for an amplifier circuit depends on several factors, including the desired gain, frequency range, and input and output impedance. FETs come in different types, such as JFETs and MOSFETs, each with their own characteristics. It is important to consider these factors and select an FET that best suits the requirements of the amplifier circuit.