- #1
raju20
- 2
- 0
Hi,
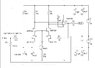
My name is raju and I am from India. I am in my first year of Degree doing Electronics and Electrical Engineering. I am having a bit of problem with this circuit I am attaching the circuit diagram.
Can anyone please tell me what is the gain of the amplifier and how can I found it. Please i would really appreciate if anyone can help me out. I am about to have my exams and i am preparing but i just can't figure out this circuit please help me..
My name is raju and I am from India. I am in my first year of Degree doing Electronics and Electrical Engineering. I am having a bit of problem with this circuit I am attaching the circuit diagram.
Can anyone please tell me what is the gain of the amplifier and how can I found it. Please i would really appreciate if anyone can help me out. I am about to have my exams and i am preparing but i just can't figure out this circuit please help me..